我上週真正開始測試python的程式碼,目前最先碰到的是讀檔的部分.
幾乎要用的每個步驟都要查找,不過也總算讓我解決了問題. 之後的文章要來處理如何精熟畫圖以及python的分析模式狀況:
我現在有三份文字檔,裡面都記錄我的rgb訊號,分別放在不同的資料夾中,必須要將他們依序讀出並且轉成我得的資訊並畫圖
問題:
1. 因為python本身讀檔方式是看.py檔在哪,就讀去同層裡的檔案,但是我必須要分別在不同資料夾中讀取,所以勢必要去告訴電腦路徑的修改
2. 因為每個檔案名稱都不同,只有附檔名是一樣的,所以要學會模糊比對(這邊學到的是正則表達式)
3. 文字檔裡面如何去篩選我要的資訊並把他們轉成字串
4. 如何做到像matlab一樣hold on 畫圖
?、
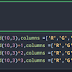
import osimport reimport numpy as npfor i in range (0,3): path = "/Users/bobobo746/Desktop/signal_test/" + "%s" %i # 先設置我之後要讀的路徑位置. 而i就是照片裡的資料夾名稱0,1,2 retval = os.getcwd() # os.gercwd 是要先找出當前的路徑 print "Current root: " ,retval os.chdir( path ) #chdir :change Directory retval = os.getcwd() print "Successfully change root: %s" % retval再來就是要如何在資料夾中找到我需要的檔案呢? 就要利用os.walk來遍歷資料夾內所有的檔案
裡面提到walk會帶出一個我當下位置所包含的東西(list),當中包含了root(根目錄),dirs(資料夾)還有files(檔案),把他們print出來確認:
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(retval): print "root: "+(root) print "dirname: %s" %(dirs) print"filesnames: %s " %(files)做模糊比對,至於正則表達式的原理我之後再補上免得久了又忘掉:
s = r'\.txt'# \. 反斜線是要取消.(點)在正則表達式的特殊含義,回歸成單純反斜線的符號for ii in range(len(files)): # Use len() to get how many files in folder t = re.search(s,files[ii]) if bool(t): print "File:%s" %files[ii] +" is read"下面是開始讀取訊號的部分:
filename = files[ii] pos = [] with open(filename, 'r') as file_to_read: lines = file_to_read.readlines() #readlines是讀取每行 p_tmp = [str(i) for i in lines] # 讀到的都當成list格式放在p_temp wow = np.append(pos,p_tmp) # 再把他們集結 wow = np.array(wow) # 轉成陣列,因為每行讀去問題,\n的字樣會出現之後便成字串會消不掉 #,所以要先轉成陣列再利用rsrip消除 最right的: \n len (wow) wow_no_slash =[] for i in range(0,24000,1): temp = wow[i].rstrip() #strip是消除空白或是\n等符號,r是右邊 ,l就是左邊 wow_no_slash = np.append(wow_no_slash,temp) wow_no_slash print wow_no_slash[51] find_R = 'Reaction_R:' find_G = 'Reaction_G:' l_list = wow_no_slash.tolist() # index is a function in list , so numpy.array needs to Transform to l_list l_list.index(find_R) l_list.index(find_G) #print l_list[52] #print l_list[2888] Signal_R = l_list[52:l_list.index(find_G)-1] print Signal_R len(Signal_R) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot(Signal_R, 'r') # End read signal parent_path = os.path.abspath("..") # Back to upper layer folder print parent_pathplt.show()# plt在最後放 =hold on以下是完整原始碼:
import os
import re
import numpy as np
for i in range (0,3):
path = "/Users/bobobo746/Desktop/signal_test/" + "%s" %i #i in here is named as file name
retval = os.getcwd()
print "Current root: " ,retval
os.chdir( path )
retval = os.getcwd()
print "Successfully change root: %s" % retval
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(retval):
print "root: "+(root)
print "dirname: %s" %(dirs)
print"filesnames: %s " %(files)
s = r'\.txt'
for ii in range(len(files)): # Use len() to get how many files in folder
t = re.search(s,files[ii])
if bool(t):
print "File:%s" %files[ii] +" is read"
# Start to read signal:
filename = files[ii]
pos = []
with open(filename, 'r') as file_to_read:
lines = file_to_read.readlines()
p_tmp = [str(i) for i in lines]
wow = np.append(pos,p_tmp)
wow = np.array(wow)
len (wow)
wow_no_slash =[]
for i in range(0,24000,1):
temp = wow[i].rstrip()
wow_no_slash = np.append(wow_no_slash,temp)
wow_no_slash
print wow_no_slash[51]
find_R = 'Reaction_R:'
find_G = 'Reaction_G:'
l_list = wow_no_slash.tolist() # index is a function in list , so numpy.array needs to Transform to l_list
l_list.index(find_R)
l_list.index(find_G)
#print l_list[52]
#print l_list[2888]
Signal_R = l_list[52:l_list.index(find_G)-1]
print Signal_R
len(Signal_R)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(Signal_R, 'r')
#plt.show()
# End read signal
print "\n"
else:
print "nothing"
parent_path = os.path.abspath("..") # Back to upper layer folder
print parent_path
plt.show()
| 這封郵件來自 Evernote。Evernote 是您專屬的工作空間,免費下載 Evernote |








0 意見:
張貼留言